Like a lot of people, I get pretty pissed off when I read that poachers kill up to 50,000 elephants each year just to harvest material that is chemically identical to my fingernails. My immediate reaction is to grab my gear, head over to Africa, and start capping fucktards. However, that’s probably going to achieve sweet fuck all. Nope, the problem runs far deeper than just the poor bastards putting their lives on the line to drop the elephant. It runs all the way from Asia to the big game parks and back again.
Recently, a non-profit organization, C4ADS, released two thoroughly detailed reports on the state of ivory smuggling. A boom in consumer demand in China has led to record levels of poaching, leading the elephant toward extinction in some parts of Africa. The reports caught my eye as they demonstrate similar methodology to that used by intelligence organizations to pull apart terrorist networks. Utilizing sophisticated analysis tools such as Palantir, they dive into the complex problem of the illicit ivory trade, from poaching to smuggling and distribution.
Before I go further, allow me to digress. A lot of smart and motivated people are fighting against the illicit wildlife trade in Africa. Former Special Forces soldiers like Damien Mander are working in an ‘advise and assist’ role with anti-poaching rangers to secure ‘high-target species’ such as rhinos and elephants. Other non-government organizations like the IFAW are implementing a broad range of strategies including targeting consumer demand. This would be considered PSYOPS or information operations in a military context, and includes paying for advertising to influence the consumer. According to the IFAW, 70 percent of the Chinese population polled believed that elephant tusks simply fall out like human teeth, and harvesting them did not result in killing the animal. They need to be educated to the bloody truth about ivory. And those eating rhino horn also need to be reminded that they could simply chew their damn nails for all the same bullshit health benefits.
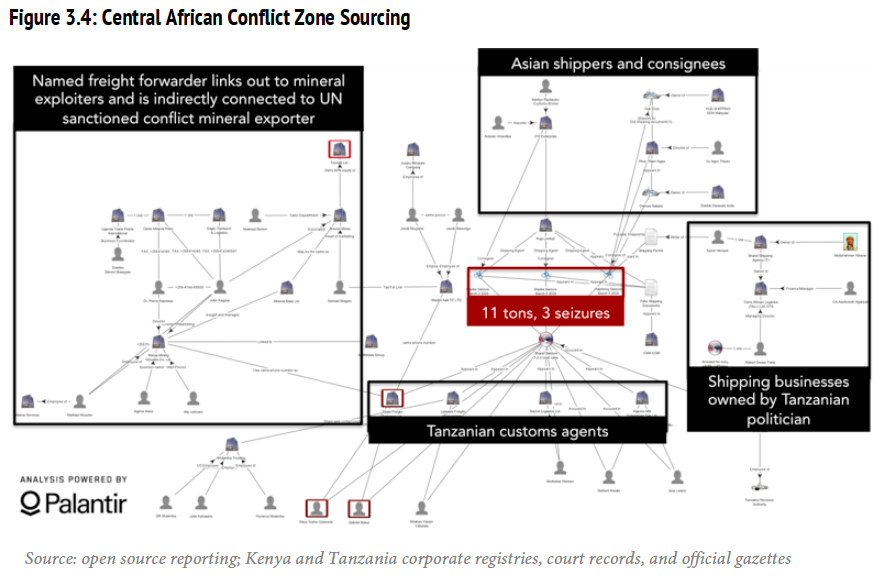
It’s important work, not just for the survival of these amazing creatures and the tourism dollars they bring to impoverished communities, but also to disrupt what has become a billion-dollar illicit industry for global organized crime. Within conflict-torn central and east Africa, numerous criminal, terrorist, and insurgent groups rely on poaching. For example, Kony’s Lord’s Resistance Army in Central Africa, Al-Shabaab in Somalia, and Janjaweed militias in Sudan all use funding from ivory that usually ends up in Chinese carving factories.
Regardless of the hard work being done, the prospects for these animals is bleak. In the years following 2006, when the Chinese government listed the ivory sector as part of the country’s ‘intangible cultural heritage’, ivory carvers and retailers have boomed. What was an attempt to save the ailing the Chinese ivory industry led to a rise in demand from the increasingly wealthy population. Now, the state-supported Chinese ivory industry relies on poaching for supply, and elephants are being culled at record rates. True, some other Asian countries like Thailand and Vietnam are also consumers, but they’re assessed as consuming far less than China.
Rhinos have already been poached out of existence in parts of central Africa, and elephants are the next in line. Current trends point to elephants being killed off at a rate of at least 30,000 per year and this number is rising. Directly combating poachers in conflict zones is an almost futile course of action. Many of the poachers are heavily armed military or guerrilla units that significantly outgun the rangers. They even use their heavy weapons and helicopters to massacre elephants. On the other side of the problem, demand-reduction strategies are unlikely to influence the Chinese population and government at a rate fast enough to ensure the elephant’s survival in many areas.

C4ADS’s reports offer some alternative strategies. I can’t cover the 160 pages of analysis or summarize all the findings here. Instead, I’ll highlight some points that might stimulate some thoughts and discussion. C4ADS advocates complementing anti-poaching and demand-reduction strategies with ‘targeting’ the smuggling networks. In military parlance, this would be referred to as ‘non-kinetic targeting,’ and some of C4ADS’s recommendations are similar to counter-proliferation (or in current jargon, counter weapons of mass effect) operations. In the case of ivory smuggling, some recommended key nodes to target are the ports in Tanzania and Kenya, most notably, Mombasa.

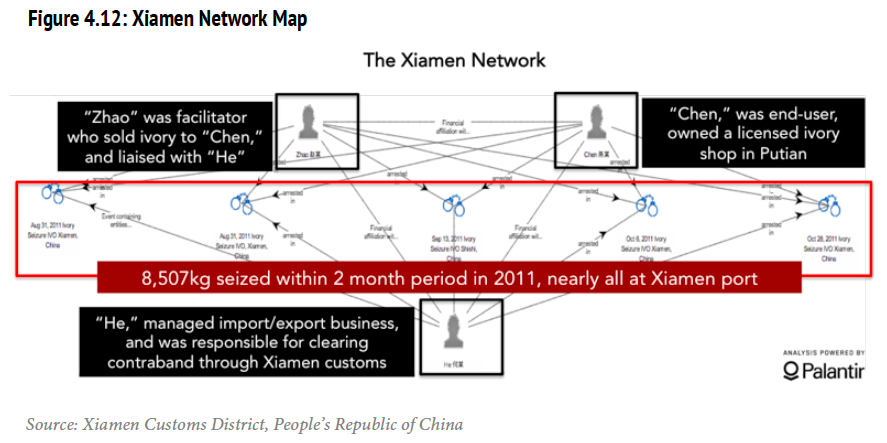
Smugglers rely predominantly on shipping to move bulk ivory from East Africa to East Asia (mainly China). C4ADS, using open sources (publicly available information) combined with anonymous interviews, was able to generate high-fidelity intelligence on this smuggling network. They highlight the issue of information existing in silos and advocate the need for an intelligence-fusion center to generate actionable intelligence. Their report leads me to believe that they have generated a great deal of intelligence, fusing data ranging from financial information, money laundering, geospatial data, and law-enforcement reports, with investigative journalism and basic link analysis. One of their most significant suggestions was that, in the absence of government bodies doing this analysis, a NGO like C4ADS could potentially do it on a contracted basis.
Already have an account? Sign In
Two ways to continue to read this article.
Subscribe
$1.99
every 4 weeks
- Unlimited access to all articles
- Support independent journalism
- Ad-free reading experience
Subscribe Now
Recurring Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
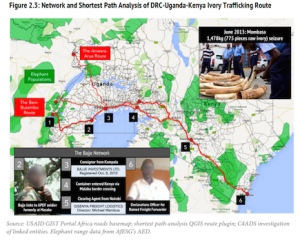
Impact could then be made through a variety of ‘non-kinetic’ options. Trusted law enforcement agencies could be tipped off to conduct seizures and arrests. If convergence is identified between ivory-smuggling networks and other forms of smuggling such as human-trafficking, drugs, or weapons, the likelihood of government response could be increased. Legitimate international shipping companies being used for smuggling could also be “incentivized to divest through reputational pressure.” Intelligence implicating corrupt government elites could be discreetly shared with international bodies to encourage the use of political pressure, sanctions, or other economic measures. Theoretically, costs would increase for the smuggling organizations, making the trade less lucrative for them and reducing poaching. And, let’s face it, as much as we may want to put warheads on foreheads, this is likely to be a more achievable and successful line of operation.
Contracted intelligence services do, however, pose a number of questions. Much of C4ADS’s information was garnered from public sources, so what if the smugglers adapt and implement stronger operational security measures? Is it appropriate for a non-government organization to step up collection to utilize other forms of intelligence? Where does one draw the line between anonymous ‘interviews’ and running a HUMINT agent network? If publicly available software is used to monitor social media or online communications, where does it cross over into the cyber-espionage realm? What happens when the billion-dollar criminal enterprise decides to retaliate? What protections do the contractors have? If the NGO needs to operate from charitable donations, how hard would it be to operate in a semi-clandestine manner in order to protect its members?
A truly effective non-government intelligence capability probably only exists in the realms of fiction right now. The covert vigilantes in my PRIMAL series of books would definitely take the fight direct to China to ‘influence’ policy makers and ivory kingpins. Yeah sure, they’d use some techniques frowned upon by not-for-profits and government agencies, but you can bet your left ball they’d be effective. If that that’s the sort of rough justice that appeals to you, you can join PRIMAL here, and I’ll let you know when a PRIMAL anti-poaching novel hits the shelves.
 So what do you think? Is a contracted intelligence-fusion center a viable strategy in the fight against illicit wildlife smuggling? Can NGOs hope to save the elephants while the Chinese government supports the ivory industry and demand for ivory is so high? Or will another few hundred thousand elephants die to satisfy the material needs of the economically upward but environmentally ignorant Chinese?
So what do you think? Is a contracted intelligence-fusion center a viable strategy in the fight against illicit wildlife smuggling? Can NGOs hope to save the elephants while the Chinese government supports the ivory industry and demand for ivory is so high? Or will another few hundred thousand elephants die to satisfy the material needs of the economically upward but environmentally ignorant Chinese?
 So what do you think? Is a contracted intelligence-fusion center a viable strategy in the fight against illicit wildlife smuggling? Can NGOs hope to save the elephants while the Chinese government supports the ivory industry and demand for ivory is so high? Or will another few hundred thousand elephants die to satisfy the material needs of the economically upward but environmentally ignorant Chinese?
So what do you think? Is a contracted intelligence-fusion center a viable strategy in the fight against illicit wildlife smuggling? Can NGOs hope to save the elephants while the Chinese government supports the ivory industry and demand for ivory is so high? Or will another few hundred thousand elephants die to satisfy the material needs of the economically upward but environmentally ignorant Chinese?












COMMENTS