The Price of Innovation: Challenges and Shortcomings
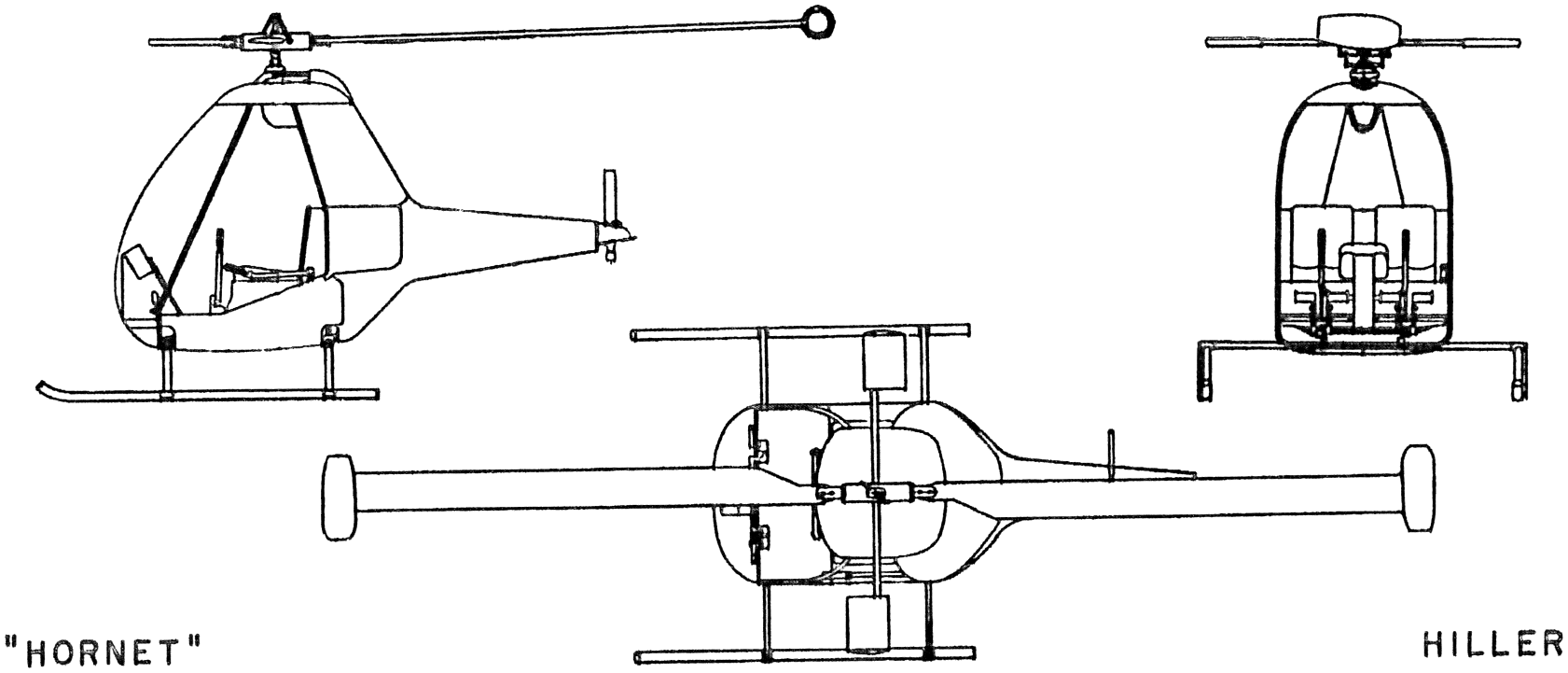
The connection between the Hiller Hornet’s design and its operational challenges was immediate.
While the ramjet engines eliminated the need for a tail rotor, thereby promising reduced weight and increased agility, they introduced significant drawbacks.
The engines created substantial drag, complicating critical maneuvers like autorotation, essential for safe landings during power loss. It reached speeds of 62 knots, respectable but underwhelming for its futuristic appearance. Its range dipped below 30 miles, a far cry from the ambitious vision.
Moreover, the Hiller Hornet’s engines were notorious for their high fuel consumption—600 pounds per hour at high power settings—which severely restricted its operational range and endurance.
Here’s a closer look at the challenges it faced:
- Drag and Inertia: The ramjet engines mounted on the tips of the blades created significant drag and inertia, hindering maneuverability and making autorotation a risky maneuver.
- Fuel Guzzling Engines: The ramjets’ high fuel consumption severely limited the Hiller Hornet’s range and practicality.
- Safety Concerns: The fiery exhaust from the ramjets posed a potential safety hazard for both the pilot and nearby personnel.
The Hiller Hornet’s limitations ultimately grounded the ambitious project.
Military Evaluation and Concluding Trials
The military took an interest in the innovative design of the Hiller Hornet and conducted several evaluations to determine its suitability for various roles, including reconnaissance and as a potential gunship.
Evaluations began with the US Army designating it the YH-32 and the US Navy christening it the XHOE-1. Both branches saw potential in Hiller Hornet’s design and are putting it through trials for various applications.
One intriguing possibility was the use of the Hiller Hornet as a gunship.
In 1957, two YH-32s were modified as YH-32As. These modifications included removing the fiberglass cockpit fairings and redesigning the tail section, all to accommodate weaponry.
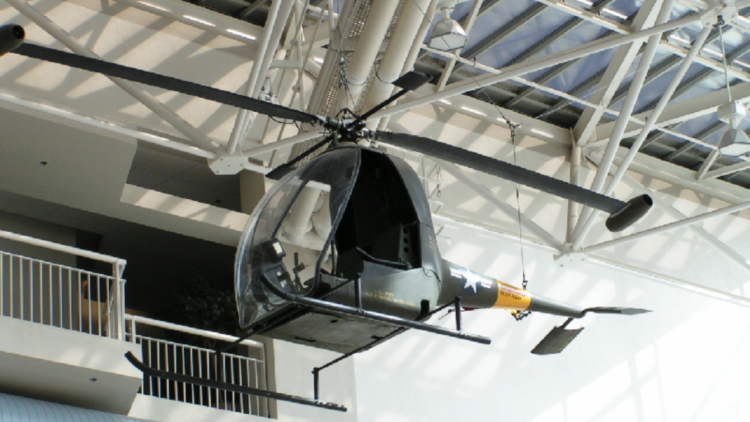
While these trials proved the Hiller Hornet could be a viable weapons platform, its performance limitations ultimately grounded this vision. No further conversions or orders were placed.
The US Army’s Development Research Center (DRC) also saw promise in the Hiller Hornet, but for a different role.
They envisioned the Hiller Hornet as a lightweight helicopter, easily airdropped for use in air rescue and reconnaissance missions.
Additionally, the DRC was interested in the Hiller Hornet’s potential as a portable, fuel-efficient observation and transport helicopter for a single pilot.
Here, the Hiller Hornet competed against the equally unconventional Jet Jeep, but both concepts were ultimately deemed obsolete, and the program was canceled.
Despite these efforts, the trials highlighted the Hornet’s performance limitations and practical challenges.
The aircraft’s high visibility at night, due to its brightly burning engines (practically painting a bullseye on the aircraft itself), and its limited range ultimately led to the decision against full-scale production.
A Legacy of Innovation and Intrigue: Beyond the Prototype
Looking beyond its limitations, the Hiller Hornet left a lasting mark on the field of aviation.
It stood as a bold experiment in rotorcraft propulsion and design simplicity that prompted engineers to rethink traditional helicopter mechanics.
The lessons learned from the Hornet’s challenges contributed to subsequent innovations in rotorcraft technology, particularly in exploring alternative methods to counteract torque without a tail rotor.
The Hornet also captured the public’s imagination, evidenced by its association with numerous UFO sightings due to its unusual appearance and fiery exhaust.
Today, the Hornet is remembered not only for its aspirations but also as a reminder of the complexities involved in redefining aviation technology.










COMMENTS